How ERP Software Transforms Production Planning in Discrete Manufacturing
Still managing production schedules with spreadsheets? Late orders, material shortages, and change orders can quickly throw your shop floor into...
23 min read
David Warford Sr. : Updated on December 8, 2025

Manufacturing success relies on more than just efficient production lines—it demands a fully integrated approach to managing all business operations. This blog explores the top ERP systems for manufacturers in 2026, showcasing how these solutions unify critical processes like production planning, inventory control, supply chain management, and financial oversight. We’ll guide you through the key features to look for in an ERP system, the substantial benefits of implementation, and strategies to navigate common challenges. Whether you’re selecting a new ERP or optimizing an existing one, this comprehensive guide will equip you with the insights needed to enhance your manufacturing operations and achieve sustainable growth.
TL;DR: Manufacturing ERP systems integrate and streamline key manufacturing processes. Their main benefits include reduced operational costs, real-time visibility, better decision-making, increased productivity, and ensured compliance. These systems help manufacturers adapt to market changes, customer demands, and regulatory requirements, driving operational excellence and supporting sustainable growth.
Recent 2025 data from Nucleus Research highlights that AI-powered analytics in modern ERP systems can improve productivity by up to 43%, a significant advantage for manufacturers. Additionally, reports indicate that average project timelines have dropped to just 9 months, allowing for faster ROI.
ERP systems integrate key processes such as inventory management, production planning, and financial management, enabling real-time visibility and control over operations. This streamlined approach not only boosts efficiency but also supports adaptability in a fast-changing market. With enhanced collaboration and data-driven decision-making, ERP systems help manufacturers stay competitive, meet customer demands, and ensure compliance with industry standards.
Manufacturing ERP also helps manufacturers quickly adapt to market changes, customer demands, and regulatory requirements by providing accurate data for informed decision-making. ERP systems optimize resource use, minimize waste, and ensure compliance with industry standards. They also support scalability, allowing businesses to grow and adapt their processes as needed.
Moreover, implementing an ERP system enhances collaboration and communication within the organization. With a single source of truth, all stakeholders, from production workers to top management, can access the same data in real time. This improves coordination, reduces errors, and enhances forecasting and planning capabilities. Ultimately, a well-integrated ERP system drives operational excellence, increases profitability, and supports sustainable growth in the complex manufacturing domain.
Choosing the right ERP system can be daunting with so many options available. Here are the top 10 manufacturing ERP systems for 2026:
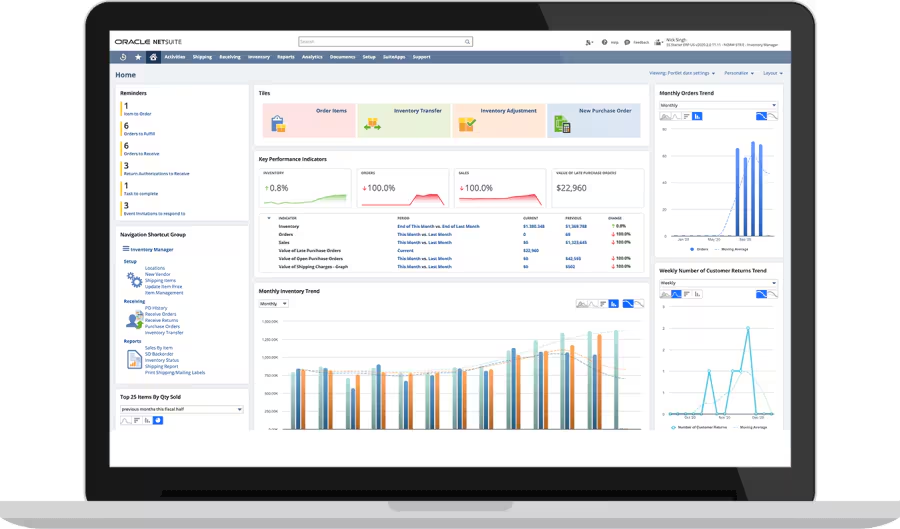
NetSuite ERP remains a leading choice for manufacturers aiming to enhance efficiency and maintain a competitive edge. This cloud-based solution offers a robust suite of tools, including financial management, inventory control, production planning, supply chain management, and CRM. By integrating these critical functions into a single platform, NetSuite enables real-time visibility and streamlined operations, which are essential for today’s manufacturers looking to optimize performance and drive growth.
One of the most exciting developments from SuiteWorld 2025 is the launch of NetSuite Next and 'Ask Oracle'. This conversational AI allows manufacturing executives to query their ERP data in plain language—generating reports, insights, and supply chain recommendations instantly without navigating complex menus.
NetSuite's ongoing focus on AI reflects its commitment to staying at the forefront of technological innovation, ensuring that manufacturers can adapt to the rapidly evolving landscape. These advancements allow businesses to focus more on strategic growth and less on routine administrative tasks, making NetSuite an even more valuable asset for manufacturers aiming to drive productivity and innovation.
However, manufacturers should be mindful of potential challenges. The complexity of initial setup, the need for customization, and the ongoing costs associated with cloud-based solutions can be significant, particularly for smaller businesses. Additionally, the integration of AI may require additional training and adaptation for teams. Despite these considerations, NetSuite’s robust feature set and continuous innovation make it a compelling choice for manufacturers looking to optimize their operations in 2026 and beyond.
-1.png?width=500&height=377&name=rubinbrown%20(4)-1.png)
Oracle ERP Cloud is a comprehensive solution designed for large and complex organizations, offering a wide range of tools to manage everything from financials and supply chain management to human capital management and procurement. As Oracle’s flagship cloud ERP product, it builds on the company's long history in enterprise software, integrating powerful data analytics and enterprise performance management capabilities.
One of the key strengths of Oracle ERP Cloud is its flexibility. Unlike more rigid systems, Oracle allows for extensive customization, enabling manufacturers to tailor the software to their specific business processes and needs. This flexibility is particularly beneficial in today’s fast-paced environment, where businesses must adapt quickly to changing market conditions. However, it’s important to note that while the system’s flexibility is a major advantage, it can also introduce complexity, potentially leading to longer and more costly implementations.
Oracle’s deep-rooted history in data management—stemming from its origins as a database company—gives it a unique edge in analytics and financial consolidation. The integration of AI and machine learning further enhances these capabilities, allowing for predictive analytics and automation across various business functions, including supply chain management, financial close processes, and customer relationship management (CRM). These advanced features make Oracle ERP Cloud a powerful tool for manufacturers looking to leverage data-driven insights to optimize their operations.
However, Oracle ERP Cloud’s complexity can be a double-edged sword. The system is designed for large, diverse organizations, which means that smaller manufacturers might find it overly complex or expensive for their needs. Additionally, the system’s relatively recent transition to the cloud has led to some gaps in functionality compared to Oracle’s more mature on-premise solutions like E-Business Suite and JD Edwards. This is particularly evident in industries with highly specialized requirements, such as complex manufacturing.
It’s also important to recognize that Oracle ERP Cloud’s implementation can be challenging. The system’s complexity, combined with the scale of the organizations it serves, has led to a track record of difficult implementations. These challenges are not necessarily a reflection of the software itself but rather the complexity of the organizations attempting to implement it. As a result, manufacturers considering Oracle ERP Cloud should carefully assess their readiness for such a comprehensive system and ensure they have the resources and expertise needed for a successful deployment.
Despite these challenges, Oracle ERP Cloud’s robust capabilities, particularly in data analytics and AI, make it an attractive option for large manufacturers looking to future-proof their operations and gain a competitive edge in the industry.
.png?width=500&height=281&name=Dynamics-365-Business-Central%20(1).png)
Microsoft Dynamics 365 Business Central is a versatile cloud-based ERP solution tailored for small to mid-sized manufacturers. As part of the broader Dynamics 365 family, Business Central integrates seamlessly with other Microsoft products, offering a comprehensive suite of tools for managing finance, supply chain, sales, and operations. Designed to be a more streamlined and cost-effective option, Business Central is ideal for manufacturers looking for a solution that balances functionality with simplicity.
One of the key strengths of Business Central is its flexibility. The system can be customized and configured to meet the specific needs of a business, which is particularly valuable for manufacturers with unique processes or requirements. Built on Microsoft’s .NET architecture, Business Central also offers robust integration capabilities, allowing manufacturers to connect their existing systems and create a cohesive technology ecosystem. This flexibility, however, can be a double-edged sword—while it allows for extensive customization, it can also lead to complexity during implementation, making it crucial for businesses to have a clear vision and strong project governance.
Another advantage of Business Central is its alignment with the broader Microsoft ecosystem. This integration means that manufacturers can easily leverage tools like Office 365, Power BI, and Azure for enhanced productivity and data analytics. Additionally, the open architecture of Business Central facilitates the use of third-party applications and add-ons, giving manufacturers the ability to tailor the system even further to their industry-specific needs.
However, while Business Central is highly adaptable, it may not be as robust as other ERP solutions when it comes to handling the demands of highly complex manufacturing operations. For manufacturers with intricate processes, such as high-volume production or complex supply chain management, Business Central may require additional customization or even integration with other specialized systems. This potential limitation makes it important for manufacturers to thoroughly assess their needs and ensure that Business Central is the right fit for their operations.
Implementation of Business Central, like other ERP systems, comes with its challenges. The flexibility that makes Business Central appealing can also introduce risks, particularly if the project lacks clear direction or if the organization resists change. Manufacturers must be prepared to manage these risks through strong change management strategies and by focusing on the broader operational and organizational impacts of the new system, rather than just the technical aspects.

Epicor Kinetic is a leading ERP solution designed specifically for manufacturing, distribution, and retail industries, with a strong emphasis on mid-market organizations. What sets Epicor Kinetic apart is its focused approach—it’s not trying to be everything to everyone but instead excels in the areas where it has deep expertise. This focus makes it a particularly strong choice for manufacturers looking for an ERP system that aligns closely with their specific industry needs.
One of the standout features of Epicor Kinetic is its flexibility in deployment options. Unlike many ERP systems that push exclusively for cloud adoption, Epicor Kinetic offers multiple deployment models, including cloud, on-premise, and hybrid. This flexibility allows manufacturers to choose the best deployment strategy for their needs, whether they’re looking to start on-premise and move to the cloud later or leverage a hybrid approach. This adaptability is particularly beneficial for businesses that may not be ready to fully commit to a cloud-only environment but want the option to transition as their needs evolve.
Epicor Kinetic also leverages low-code technology, which is relatively rare in the ERP space. This means that manufacturers can customize and personalize the software without the need for extensive coding or risking over-customization. The low-code approach provides the best of both worlds—flexibility and ease of use—without the common pitfalls of heavy customization, such as difficulty with future upgrades.
Another significant strength of Epicor Kinetic is its product configurator, which is particularly valuable for manufacturers engaged in engineer-to-order or make-to-order processes. The product configurator allows sales reps to customize product offerings during the sales process, which then seamlessly translates into the necessary bill of materials, MRP, and manufacturing processes. This capability has long been a strength of Epicor, making it a go-to solution for manufacturers with complex product configuration needs.
In terms of implementation, Epicor Kinetic is known for its relatively quick and cost-effective deployment compared to other ERP systems. The focused nature of the software, particularly its deep functionality in manufacturing, distribution, and retail, means that businesses can often implement the system with less time, money, and risk. This efficiency allows manufacturers to realize value from their investment sooner, making Epicor Kinetic a high-value choice for mid-market companies.
However, it’s important to note some of the limitations of Epicor Kinetic. While it excels in its target industries, it may not be the best fit for companies with diverse operations or those outside of its core focus areas. Additionally, Epicor Kinetic is less robust in areas like CRM and human capital management (HCM) compared to other ERP solutions. This narrower focus can be a drawback for manufacturers with broad or complex needs across various business functions.
Moreover, while Epicor has made significant strides in improving its partner network and financial stability over the years, it still may not have the breadth of support resources that some larger ERP vendors offer. Manufacturers considering Epicor Kinetic should carefully evaluate their specific needs and ensure that they have access to the necessary implementation and support resources.
Epicor Kinetic is a strong contender for mid-market manufacturers, particularly those in the engineer-to-order or make-to-order space. Its flexibility in deployment, low-code customization, and robust product configurator make it an appealing choice for companies looking to streamline their operations and gain a competitive edge. However, it’s essential to consider the system’s limitations and ensure it aligns with your company’s broader strategic goals.

Infor CloudSuite is a versatile ERP solution tailored for the manufacturing, distribution, and retail industries. Known for its deep industry-specific functionality, Infor CloudSuite is particularly well-suited for sectors such as food and beverage, aerospace and defense, and industrial manufacturing. This specialization positions it as a leading choice for companies seeking an ERP system that aligns closely with their unique industry demands.
One of the key strengths of Infor CloudSuite is its flexibility. Unlike some of the larger ERP vendors like SAP or Oracle, Infor CloudSuite offers a more adaptable solution that can be customized to meet the specific needs of a business. This flexibility is partly due to Infor’s history of strategic acquisitions, such as Lawson and Baan, which have been integrated into the CloudSuite ecosystem. These acquisitions have allowed Infor to build a diverse set of capabilities that cater to a wide range of industries, all within a unified cloud-based platform.
However, this extensive functionality comes with some trade-offs. While Infor CloudSuite excels in many areas, the user interface (UI) has been noted as somewhat outdated compared to more modern ERP systems like NetSuite or Microsoft Dynamics 365. This can impact user adoption, as employees might find the system less intuitive and harder to navigate. Despite this, the functional capabilities of Infor CloudSuite remain strong, particularly in areas such as manufacturing, distribution, and retail, where it offers advanced features like predictive analytics for supply chain management and sophisticated configure, price, quote (CPQ) functionality.
Infor CloudSuite is particularly strong in managing complex manufacturing processes, especially for make-to-order or engineer-to-order environments. The system’s ability to handle intricate product configurations and translate them seamlessly into manufacturing processes is a significant advantage for manufacturers with complex production needs. Additionally, Infor CloudSuite’s capabilities in retail, particularly in fashion and apparel, are noteworthy. The system’s ability to manage different sizes, colors, and other product variations within the supply chain is a critical feature for businesses in these industries.
Another advantage of Infor CloudSuite is its focus on innovation and continuous improvement. The recent full acquisition of Infor by Koch Industries has provided a substantial boost to Infor’s research and development (R&D) efforts. This infusion of resources is helping to drive further enhancements and innovations within the CloudSuite platform, ensuring that it remains competitive with other top-tier ERP solutions.
However, potential users should be aware of some challenges associated with Infor CloudSuite. The product roadmap can be complex and sometimes unclear, largely due to the number of legacy systems and products that Infor has acquired over the years. As Infor continues to migrate these legacy systems into the CloudSuite environment, businesses must carefully assess whether they are adopting the most modern and forward-looking components of the system or relying on older, potentially less supported technology.
Infor CloudSuite offers a powerful and flexible ERP solution tailored to the needs of specific industries, particularly manufacturing, distribution, and retail. Its deep functionality, combined with ongoing innovation, makes it a compelling choice for businesses looking for an industry-focused ERP system. However, organizations should carefully evaluate the user interface, the clarity of the product roadmap, and ensure that the system aligns with their long-term strategic goals before making a decision.
.webp?width=600&height=347&name=general_screenshots-1%20(1).webp)
Acumatica stands out as a top ERP solution for manufacturing businesses, providing a cloud-based platform that covers all key areas of the manufacturing process. Acumatica’s Manufacturing Edition is designed to streamline operations, improve efficiency, and support business growth. It includes modules for production management, material requirements planning (MRP), inventory control, and bill of materials (BOM) management, making it ideal for manufacturers aiming to optimize processes and enhance supply chain visibility.
A key feature of Acumatica is its real-time data capabilities, enabling quick, informed decision-making. Its open architecture allows for easy integration with other business systems, offering the flexibility and scalability needed as a business expands. The user-friendly interface and mobile access ensure teams can access important information from anywhere, keeping operations smooth both on the shop floor and remotely.
Acumatica is also effective in managing complex manufacturing workflows, such as make-to-order, make-to-stock, engineer-to-order, and project-centric manufacturing. This versatility makes it suitable for small to large manufacturing businesses. The system’s advanced reporting and analytics tools help users track key performance indicators (KPIs), identify trends, and make data-driven decisions to boost operational efficiency.
However, potential downsides include the higher implementation costs, especially due to customization and integration needs. The platform’s flexibility can also introduce complexity during the initial setup, requiring significant support and training, particularly for businesses moving from a legacy system or with limited IT resources. Despite these challenges, Acumatica is a leading choice for manufacturers looking for a robust, scalable ERP solution in 2024.

IFS ERP is a robust solution that has steadily gained traction, particularly in industries such as construction, utilities, and industrial manufacturing. While it may not have the same level of brand recognition as some of the more established ERP giants, IFS is a serious contender, especially for mid-market organizations looking for industry-specific capabilities and flexibility.
One of the key strengths of IFS ERP is its focused approach. Unlike ERP systems that aim to be one-size-fits-all, IFS is designed with specific industries in mind, making it an ideal choice for companies in sectors like construction, utilities, and field service management. Its project management and project costing capabilities are particularly strong, catering to the needs of companies involved in complex projects, whether they are commercial or residential construction, infrastructure development, or utilities.
Another area where IFS excels is in field service management. IFS provides robust mobile workforce capabilities, allowing companies with field service technicians to track data and improve customer service effectively. This focus on customer experience, especially in field-driven operations, sets IFS apart from other ERP systems that may prioritize back-office functions like financials and inventory management.
Flexibility is another significant strength of IFS ERP. The system allows for customization without affecting the core software, thanks to its innovative programming layer. This means that companies can tailor the software to their specific needs without compromising future upgrades or system stability. This level of flexibility is crucial for mid-market companies that need a solution to grow and adapt to their changing needs.
Despite these strengths, IFS ERP does have some limitations. It may not be the best fit for organizations with highly complex distribution networks or those requiring advanced financial consolidation and reporting capabilities. While IFS does offer solid project-related financials, other ERP systems might provide more sophisticated financial tools, particularly for large, multinational organizations.
Moreover, while IFS is known for its flexibility and customer focus, it has a smaller partner network compared to larger ERP vendors. This can be a challenge for companies looking for extensive implementation support and technical expertise. However, IFS is actively working to expand its partner ecosystem, which should help mitigate this limitation over time.
Looking to the future, IFS continues to focus on its core strengths, particularly in field service management and mid-market companies. The company's recent acquisitions in the field service space demonstrate its commitment to this area. Additionally, IFS's leadership has shown a pragmatic approach to cloud deployment, acknowledging that cloud may not always be the best option for every customer and continuing to offer both on-premise and cloud solutions.
IFS ERP is a compelling option for mid-market companies in industries like construction, utilities, and industrial manufacturing. Its industry-specific capabilities, flexibility, and customer-focused approach make it a strong contender for companies looking for a tailored ERP solution. However, organizations with complex financial or distribution needs should carefully evaluate whether IFS is the best fit for their requirements.
-1.png?width=500&height=309&name=rubinbrown%20(6)-1.png)
SAP S/4HANA is one of the most widely used ERP systems in the world, particularly among large, complex organizations with multinational operations. As SAP’s flagship product, S/4HANA represents a significant evolution from its predecessors, offering advanced features and capabilities designed for the cloud, although it can also be deployed on-premise. This flexibility in deployment options allows organizations to choose the model that best fits their current needs and future growth plans.
One of the key differentiators of S/4HANA is its foundation on the HANA database, a powerful in-memory database developed by SAP. This architecture enables real-time processing and analytics, providing businesses with faster insights and decision-making capabilities. The HANA platform also reduces dependency on third-party databases like Oracle, streamlining the overall infrastructure and enhancing performance.
S/4HANA is particularly well-suited for large, complex organizations, such as those in manufacturing, that require robust functionality across diverse business processes. It excels in scenarios where there are intricate supply chains, multiple business units, and a need for detailed financial reporting across various geographies. The system’s advanced capabilities in areas like artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning further enhance its appeal by enabling predictive analytics and automation across key functions, such as supply chain management and financial operations.
However, while S/4HANA offers significant advantages, it also presents challenges, particularly in terms of implementation complexity. Organizations adopting S/4HANA often face a steep learning curve, especially when migrating from legacy SAP systems like ECC. The transition to S/4HANA involves not only a shift in technology but also significant changes to business processes and organizational structures, which can make the implementation process both time-consuming and costly.
One of the critical challenges with S/4HANA is that, despite its advanced features, the system is still evolving. Compared to its predecessor, ECC, S/4HANA is a relatively new platform, and not all legacy functionalities have been fully developed or migrated. This ongoing development means that businesses need to carefully assess the system’s capabilities and identify any potential gaps that could impact their operations. Additionally, the complexity of the system and the breadth of its capabilities can make it difficult to implement without significant investment in change management and project governance.
To successfully implement S/4HANA, organizations should take several key steps. First, it is crucial to conduct a thorough evaluation to ensure that S/4HANA is the right fit for their specific needs. This includes comparing S/4HANA against other ERP systems like Oracle or Microsoft Dynamics to ensure that it aligns with the organization’s strategic goals. Second, aligning the project team and stakeholders is essential for driving the project forward and ensuring that everyone is working towards the same objectives. Third, a strong focus on change management is vital to address the cultural and operational shifts that will occur during the implementation. Finally, setting realistic expectations regarding timelines and budgets is critical to avoid the common pitfall of underestimating the resources required for a successful S/4HANA deployment.
SAP S/4HANA is a powerful ERP solution that offers significant benefits for large, complex organizations, particularly in manufacturing. Its advanced features, real-time processing capabilities, and flexibility in deployment make it a compelling choice for companies looking to modernize their operations. However, the complexity of the implementation process and the evolving nature of the platform require careful planning and a strong commitment to change management to ensure a successful outcome.

Plex ERP is a cloud-based enterprise resource planning system designed primarily for manufacturers, with a strong emphasis on the automotive sector. Originating as a Manufacturing Execution System (MES), Plex has evolved into a comprehensive ERP solution while maintaining its core strength in production and shop floor management. The platform is particularly well-suited for North American automotive suppliers, especially those aligned with the Toyota production system, offering deep industry-specific functionality that supports lean manufacturing processes.
One of the key differentiators of Plex ERP is its cloud-native architecture, which allows for continuous updates, scalability, and flexibility. This cloud-first approach ensures that businesses can take advantage of the latest features without the need for extensive on-premise infrastructure. Plex’s user interface is modern and intuitive, making it easier for users to navigate complex manufacturing processes, manage real-time production data, and maintain compliance with industry standards.
Plex’s MES capabilities are among the most robust in the market, providing real-time production monitoring, advanced scheduling, and comprehensive quality management features. These capabilities are critical for industries that require stringent production controls and traceability, such as automotive and food and beverage manufacturing. The platform’s ability to integrate deeply with shop floor machinery and manage production workflows positions it as a leader in the MES space within its target industries.
However, while Plex excels in manufacturing and MES, its broader ERP functionality, particularly in areas like financial management and supply chain integration, has been noted as less developed compared to other leading ERP systems. The accounting functions within Plex have been described as an afterthought, which can be a limitation for businesses that require strong financial reporting and comprehensive supply chain management capabilities. Additionally, Plex's heavy focus on the automotive sector means that it may not be the best fit for industries with different operational needs, such as aerospace or complex engineer-to-order manufacturing.
Implementing Plex ERP can also present challenges, particularly due to its reliance on customers to manage a significant portion of the deployment process. While Plex consultants provide guidance and support, the expectation is that customers will perform much of the heavy lifting, which can be a daunting task for organizations without extensive internal ERP expertise. Furthermore, integration with shop floor equipment, while supported, often requires third-party solutions, adding complexity and potential costs to the implementation.
For organizations deeply embedded in the automotive supply chain, particularly those focused on the Toyota ecosystem, Plex ERP offers a compelling solution that aligns closely with industry requirements. Its MES capabilities, combined with a modern cloud-based platform, make it a powerful tool for managing production processes and ensuring compliance with automotive industry standards. However, companies outside of this niche, or those requiring more robust financial and supply chain capabilities, may find that Plex does not fully meet their needs.
Plex ERP is a specialized solution that offers significant benefits for automotive manufacturers and other select industries focused on lean manufacturing and real-time production management. Its advanced MES features and cloud-native architecture make it a strong contender for businesses in these sectors. However, potential users should carefully evaluate the platform's ERP functionalities and consider the demands of the implementation process to ensure that Plex is the right fit for their broader business needs.
Sage X3 is an ERP solution designed for small to mid-sized manufacturers, distributors, and service businesses. It improves operational efficiency by providing flexible functionality in financial management, supply chain, production, inventory, and customer relationship management (CRM). Its user-friendly, scalable, and cost-effective nature makes it suitable for businesses aiming to grow.
A key feature of Sage X3 is its adaptability. It allows manufacturers to customize the software to fit their processes with minimal coding. The platform supports multiple languages, currencies, and locations, making it ideal for businesses with global operations or international expansion plans. The system's easy-to-use interface and robust reporting tools offer real-time business insights, helping manufacturers make informed decisions, increase productivity, and quickly adapt to market changes.
Sage X3 supports process, discrete, and mixed-mode manufacturing, and is beneficial for industries like food and beverage, chemicals, pharmaceuticals, and industrial equipment, especially those with strict regulatory requirements.
Challenges with Sage X3 include its complex implementation, especially for companies without dedicated IT resources, and potential additional costs for integrating third-party applications. Ongoing training and support are also necessary to fully utilize its features.
When selecting manufacturing ERP software, it's essential to focus on features that enhance efficiency, productivity, and adaptability to the complex needs of the manufacturing industry. Key areas to consider include production management, inventory and supply chain management, and financial management and reporting.
Production Management
For production management, seek out tools that support detailed scheduling, planning, and real-time monitoring of production processes. Look for solutions that offer robust shop floor automation and integration capabilities, allowing seamless data capture directly from machinery and production lines. This integration is crucial for providing insights into production performance, reducing downtime, and enabling data-driven decision-making. Effective production management features should also include capacity planning and advanced scheduling to optimize resource allocation and ensure smooth operations, ultimately enhancing overall output and reducing operational bottlenecks.
Inventory and Supply Chain Management
In the world of inventory and supply chain management, advanced tracking capabilities for raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods are non-negotiable. The ERP system should offer real-time visibility, automated reordering, and comprehensive traceability to maintain optimal inventory levels and minimize carrying costs. Additionally, robust supply chain management features are necessary to manage complex procurement processes, coordinate with suppliers, and ensure the timely delivery of materials. This helps maintain a seamless flow of goods, preventing production delays and ensuring that manufacturing operations are always aligned with demand.
Financial Management and Reporting
For financial management and reporting, the ERP system should provide integrated financial modules that cover accounting, budgeting, and cost management. Advanced reporting and analytics tools are vital for tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), analyzing financial data, and gaining insights into profitability and cost-efficiency. The ability to perform real-time financial analysis and generate detailed reports supports strategic planning by providing a clear picture of the organization’s financial health and operational performance. These features enable businesses to make informed decisions that drive growth and improve profitability, while also ensuring compliance with industry-specific financial regulations.
Scalability and Flexibility
An additional feature to consider is the scalability and flexibility of the ERP system. As your manufacturing operations grow, your ERP system should be able to scale with you, whether through adding users, expanding to new production sites, or incorporating additional modules. Flexibility in deployment options, such as cloud-based or on-premise solutions, can also be a critical factor, allowing your business to adapt to changing technological and operational requirements. The ERP system should offer configurability to meet specific business needs without extensive customization, reducing the complexity and cost of future upgrades.
Ecosystem and Vendor Support
Finally, consider the ecosystem and vendor support available for the ERP system. The strength of the vendor’s ecosystem—including the availability of system integrators, consultants, and support resources—can significantly impact the success of your ERP implementation. Opting for a system with a well-established support network ensures that you have access to the necessary expertise and resources to address any challenges that may arise during and after implementation. This is particularly important for smaller manufacturers who may require more hands-on support and guidance throughout the process.
Implementing an ERP system in manufacturing can greatly improve operational efficiency and productivity. One primary benefit is enhanced real-time visibility across all business aspects. With an integrated ERP system, manufacturers can monitor production processes, inventory levels, and supply chain activities in real time, facilitating informed decision-making. This visibility helps identify bottlenecks, reduce downtime, and optimize resource allocation, resulting in smoother operations and increased output.
Another major advantage of ERP implementation is improved cost control. By automating and streamlining business processes, ERP systems reduce manual errors and administrative overhead, leading to more accurate financial reporting and better cost management. For instance, ERP systems can optimize inventory management by ensuring materials are ordered just in time, reducing excess stock and associated carrying costs. Better coordination with suppliers and real-time tracking of material usage can further cut costs.
ERP systems also enhance regulatory compliance and data security. Manufacturing businesses must adhere to various industry standards and regulations, which can be challenging to manage manually. ERP systems provide built-in compliance features, such as audit trails and standardized reporting, ensuring businesses meet regulatory requirements efficiently. Additionally, ERP systems offer robust data security measures, protecting sensitive information from breaches and ensuring data integrity. With automated compliance and enhanced security, manufacturers can focus on their core activities, confident that they are meeting all legal and regulatory obligations.
Choosing the best manufacturing ERP for your business involves careful consideration of several critical factors. First, assess your business needs and objectives. Identify the specific challenges and requirements of your manufacturing operations, such as production scheduling, inventory management, supply chain coordination, and regulatory compliance. Understanding these needs will help you determine which ERP features are essential for your business. According to the 2025 ERP Report by Panorama Consulting, 72.6% of organizations have now deployed AI capabilities within their ERP to drive efficiency, while 83% reported their projects met ROI expectations.
Next, evaluate the scalability and flexibility of the ERP solutions under consideration. As your business grows, your ERP system should be able to accommodate increased data volumes, additional users, and more complex processes. Cloud-based ERP solutions often offer greater scalability and flexibility compared to on-premise systems. They can be easily updated and expanded as your business evolves. Furthermore, customizable ERP systems allow you to tailor functionalities to meet your specific requirements, ensuring that the system remains relevant and effective over time.
Finally, consider the total cost of ownership (TCO), including implementation, customization, training, and ongoing maintenance. While the initial investment in an ERP system can be substantial, the long-term benefits, such as increased efficiency, reduced operational costs, and improved decision-making, can outweigh these expenses. Nucleus Research studies found that organizations deploying ERP solutions were able to recoup their investments effectively, with new data showing that for every $1 invested in modern ERP, businesses see an average return of $1.52 (52% ROI), often achieving payback in under 2.5 years.
Choosing between cloud ERP and on-premise ERP for manufacturing requires understanding the key differences and benefits of each option.
Cloud ERP systems
Hosted on the vendor's servers and accessed via the internet. They offer lower upfront costs, scalability, and automatic updates. Manufacturers benefit from reduced IT overhead as there's no need to maintain physical servers or manage software upgrades. Cloud ERP also allows access from any location with internet access, enabling remote work and collaboration.
On-premise ERP systems
Installed locally on a company's own servers and infrastructure. This option offers greater control over customization, security, and data management. It is suitable for manufacturers with stringent data security requirements or limited internet connectivity, as it operates independently of external factors. However, on-premise ERP involves higher initial costs for hardware and software, along with ongoing maintenance and upgrade expenses. Panorama Consulting found that 59% of businesses reported higher total cost of ownership for on-premise ERP compared to cloud ERP.
The decision between cloud ERP and on-premise ERP depends on the specific needs and resources of the manufacturing business. Cloud ERP is ideal for companies seeking flexibility, lower upfront costs, and minimal IT involvement. It allows for quick deployment and scalability, making it suitable for dynamic and growing businesses. On-premise ERP, while offering more control and customization, is better for companies with significant IT resources and specific security or compliance requirements. Evaluating these factors will help manufacturers choose the ERP deployment model that best aligns with their operational goals and long-term strategy.
Implementing an ERP system in manufacturing comes with several challenges, but understanding these obstacles and their solutions can lead to a smoother process.
Resistance to Change
Employees often resist new ERP systems because they require changes to existing workflows and processes. To address this, invest in comprehensive training and change management. Engage employees early, communicate the benefits clearly, and provide ongoing support to ease the transition and foster acceptance.
Data Migration
Moving data from legacy systems to a new ERP platform can be complex and time-consuming, with risks of data loss or inaccuracies. Mitigate these risks with thorough planning and data cleansing. Conduct a detailed audit of existing data, remove duplicates, and ensure data accuracy before migration. Utilize data migration tools and work closely with the ERP vendor or an experienced implementation partner to ensure a successful data transfer.
Customization and Integration
Tailoring the ERP system to fit unique processes and integrating it with existing software applications can be challenging. Over-customization can lead to increased complexity and costs. Prioritize critical customizations that align with business goals and leverage the ERP system's standard functionalities. Ensure robust integration capabilities and work with vendors that offer flexible APIs to facilitate smoother integration with other business systems.
Implementing a manufacturing ERP system is a strategic investment that reduces operational costs and enhances real-time visibility and decision-making. By integrating processes like inventory management, production planning, and supply chain operations, ERP systems streamline workflows, boost productivity, and ensure compliance. This approach optimizes resource use, minimizes waste, and helps manufacturers adapt to market changes and regulatory demands. Embracing ERP technology drives operational excellence and supports sustainable growth in the competitive manufacturing environment.
The decision to implement a new ERP system is too important to leave to chance. Partnering with an ERP evaluation team ensures expert advice, unbiased analysis, and strategic planning, making it an investment in your company's long-term success. Begin your ERP conversion journey with the team at RubinBrown today.


Still managing production schedules with spreadsheets? Late orders, material shortages, and change orders can quickly throw your shop floor into...

6 min read
The production schedule is set, but a machine on Line 3 just went down. Simultaneously, a key supplier shipment is late, and a priority customer...
5 min read
Manufacturing IT leaders are under increasing pressure. Your traditional Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) systems are excellent at recording what...